The most prominent distinction between LLaMA-1 and LLaMA-2 lies
in the incorporation of higher-quality corpora, a pivotal factor
contributing to significant performance enhancements in LLaMA-2.
This, coupled with its commercial availability, extends the
potential for creative applications of large models within the
open-source community.
Nevertheless, it’s widely
recognized that the cost of pre-training large models from
scratch is exorbitant, often humorously referred to as a domain
accessible only to those with “50 million dollars” to spare.
This deters many companies and developers, so how can we build
our own large models at a lower cost?
Being at the
forefront of cost reduction and efficiency enhancement for large
models, the
Colossal-AI
team maximizes the core capabilities of LLaMA-2. Through
innovative training techniques, Colossal-AI has achieved
remarkable results by utilizing only approximately
0.0085 trillion tokens of data, investing 15 hours, and
incurring training costs in the range of a few hundred
dollars. This strategy has yielded a high-performance Chinese LLaMA-2
model that consistently outperforms competitors across multiple
evaluation benchmarks.
In contrast to the original
LLaMA-2, Colossal-AI’s model not only enhances Chinese language
capabilities but also further refines its proficiency in
English. Remarkably, it exhibits performance levels that rival
state-of-the-art (SOTA) models of similar scale within the
open-source community.
Underpinning Colossal-AI’s
approach are steadfast open-source principles. As a result, this
model is made
accessible without any commercial restrictions, with complete
transparency extended to the entire training process, code,
and model weights. In conjunction with this, Colossal-AI offers the
comprehensive evaluation framework, ColossalEval, facilitating
cost-effective reproducibility.
Moreover, the
methodologies developed by Colossal-AI can be
readily applied across various domains,
facilitating the economical construction of large models that
are pre-trained from scratch.
Open-source code and
weights are available at :
https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI

Performance
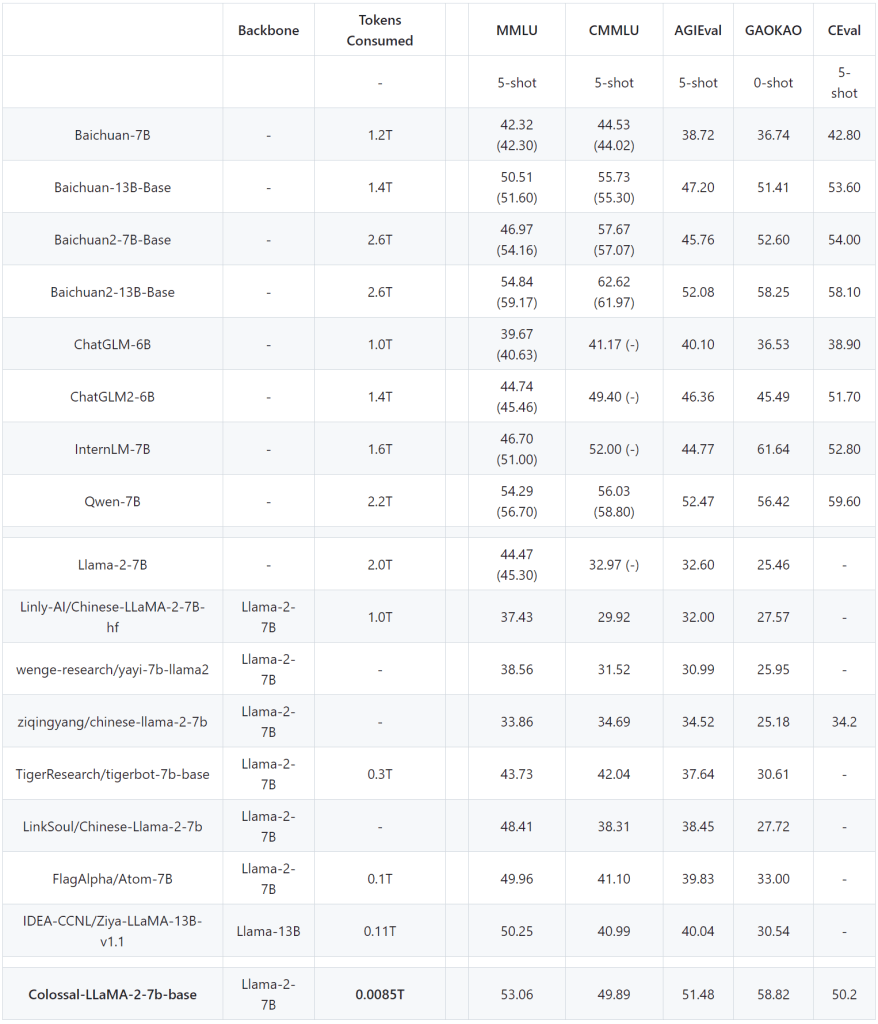
Note: Based on ColossalEval scores, the scores in parentheses
are from the official leaderboard scores of the corresponding
models, and C-Eval scores are from the official Leaderboard.
In
commonly observed English evaluation rankings, it can be
observed that in the MMLU ranking, Colossal-LLaMA-2-7B-base,
with the support of low-cost continual pre-training, has
overcome the problem of catastrophic forgetting. Its
capabilities have steadily improved (44.47 → 53.06), showcasing
outstanding performance among all 7B-scale models.
In
the Chinese rankings, the primary comparisons were made against
CMMLU, AGIEVAL, GAOKAO, and C-Eval. The performance of
Colossal-LLaMA-2 significantly outshines other Chinese
localization models based on LLaMA-2. Even when compared to
other renowned models that employ Chinese language corpora and
may cost millions of USD for training from scratch,
Colossal-LLaMA-2 still stands out at the same scale. Notably,
when compared to the original LLaMA-2, it has made a remarkable
leap in Chinese language proficiency (CMMLU: 32.97 → 49.89).
In
addition,
fine-tuning through methods like SFT and LoRA has limitations
in effectively infusing knowledge and capabilities from the
base model. It doesn’t satisfactorily meet the requirements for
constructing high-quality domain-specific knowledge or
specialized model applications.
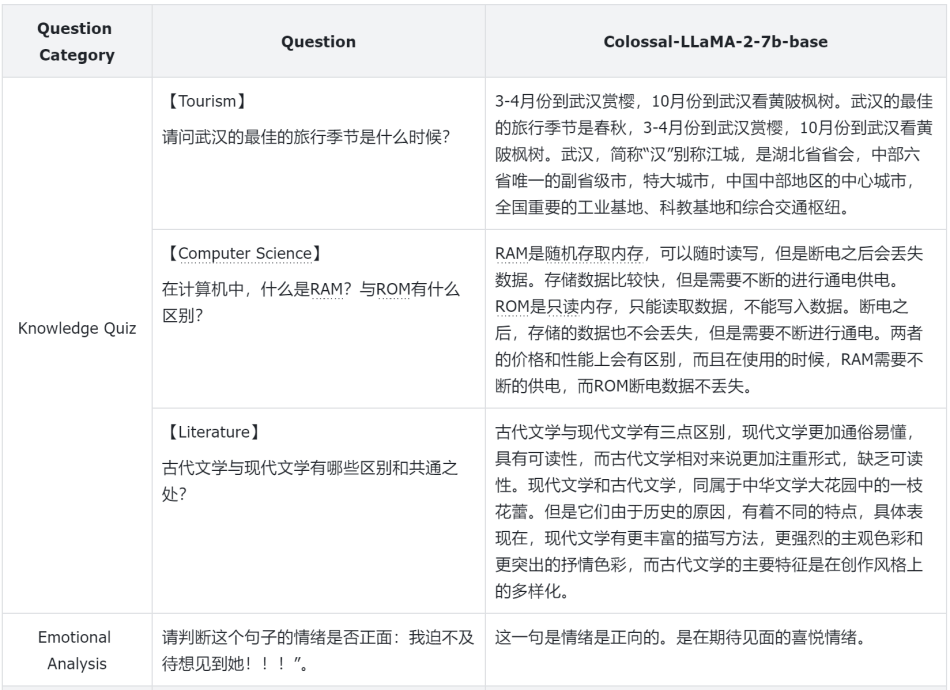
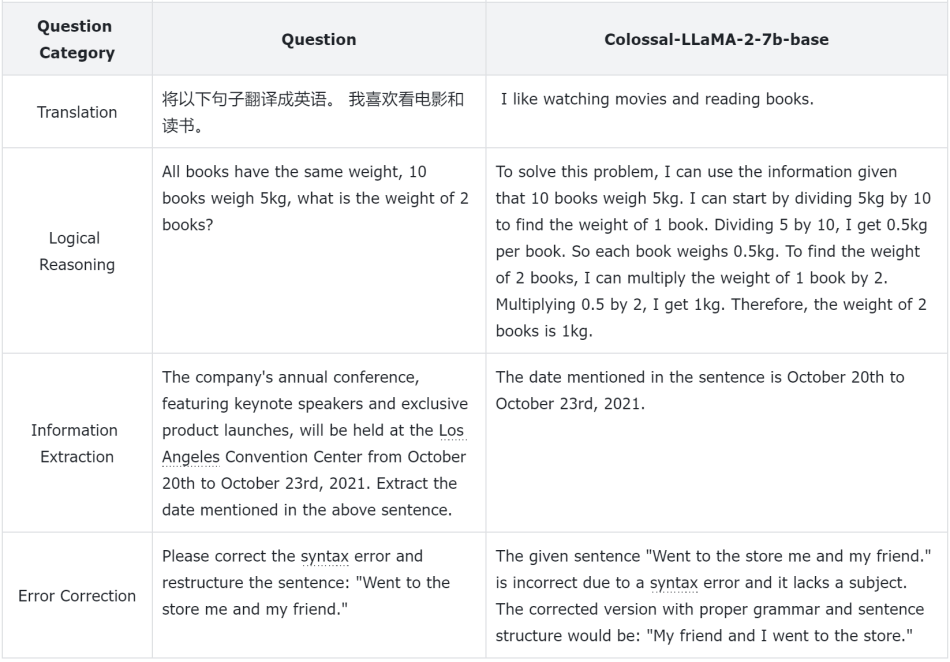
To better evaluate
the performance of the models, the Colossal-AI team relies not
only on quantitative indicators but also conducts manual
evaluations on different model aspects. Below are some examples:
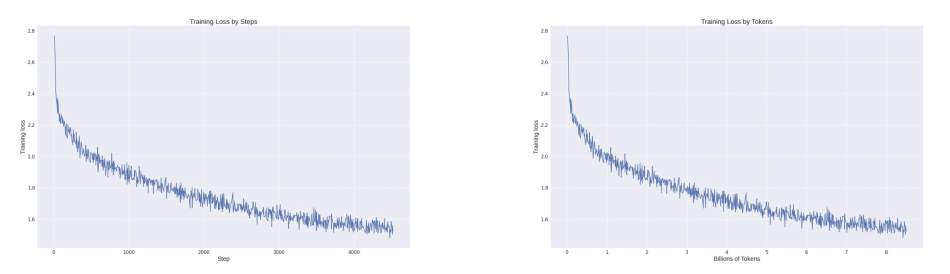
Looking at the entire training loss record, it’s evident that while harnessing the cost-effective capabilities of the Colossal-AI system, the model’s convergence is also well-preserved. With a training dataset of only about 8.5 billion tokens and computational costs in the range of hundreds of dollars, the model achieves such remarkable results. In contrast, many large-scale models available in the market require training with several trillion tokens to ensure effectiveness, incurring significantly higher costs.
So, how did the Colossal-AI team manage to reduce training costs and achieve such impressive results?
Vocabulary Expansion and Model Initialization
LLaMA-2’s original vocabulary was not specifically optimized for
Chinese and had a limited set of Chinese words, resulting in
insufficient comprehension of Chinese language data.
Consequently, the first step involved expanding the vocabulary
of LLaMA-2.
The Colossal-AI team discovered that:
- Vocabulary expansion not only significantly improved the efficiency of encoding string sequences but also enriched the encoded sequences with more meaningful information. This, in turn, proved highly beneficial for document-level encoding and understanding.
- However, due to the limited volume of continual pre-training data, an extensive expansion of the vocabulary could result in certain words or combinations lacking practical meaning, making it challenging to learn them effectively from the continual pre-training dataset and impacting the final performance.
- An excessively large vocabulary would increase the number of embedding-related parameters, affecting training efficiency.
Therefore, after conducting numerous experiments while
considering both training quality and efficiency, the
Colossal-AI team decided to expand the vocabulary from the
original 32,000 words in LLaMA-2 to 69,104.
With the
expanded vocabulary in place, the next step involved
initializing the embeddings based on the original LLaMA-2 for
the new vocabulary. To facilitate a seamless transition of
capabilities from the original LLaMA-2 to the Chinese LLaMA-2
while ensuring that the English proficiency remains unaffected
in the initial state, the Colossal-AI team employed mean
initialization of the new embeddings using the weights from the
original LLaMA-2. This approach not only preserved the English
language capabilities but also facilitated the smooth transfer
of these capabilities to the Chinese language model.
Data Construction
To further reduce the cost of training, high-quality data plays
a key role, especially for continual pre-training which has
strict requirements for the quality and distribution of data. In
order to better filter high-quality data, the Colossal-AI team
has constructed a complete data cleaning system and toolkit for
selecting higher quality data for continual pre-training.
The
following image shows the complete data governance process of
the Colossal-AI team:
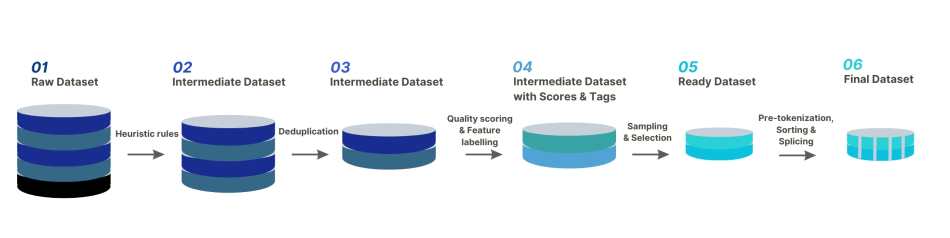
In addition to conducting heuristic selection and deduplication
of data, scoring and classification filtering were also applied
to key data. Suitable data plays a crucial role in stimulating
the Chinese capabilities of LLaMA-2, while simultaneously
overcoming the catastrophic forgetting problem in English.
Finally,
in order to improve training efficiency for data on the same
topic, the Colossal-AI team sorted the data by length and
concatenated it according to the maximum length of 4096.
Training Strategy
Multi-stage Training
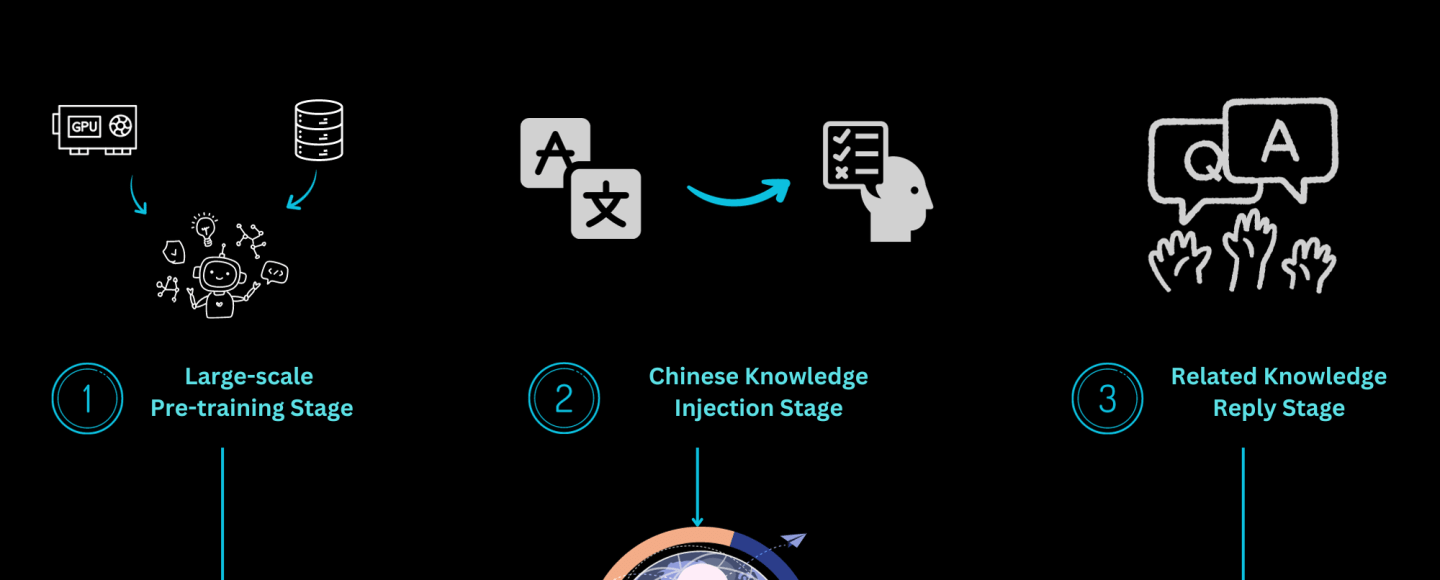
In terms of training, given the characteristics of continual pre-training, the Colossal-AI team designed a multi-stage, hierarchical continual pre-training scheme, dividing the training process into three stages:
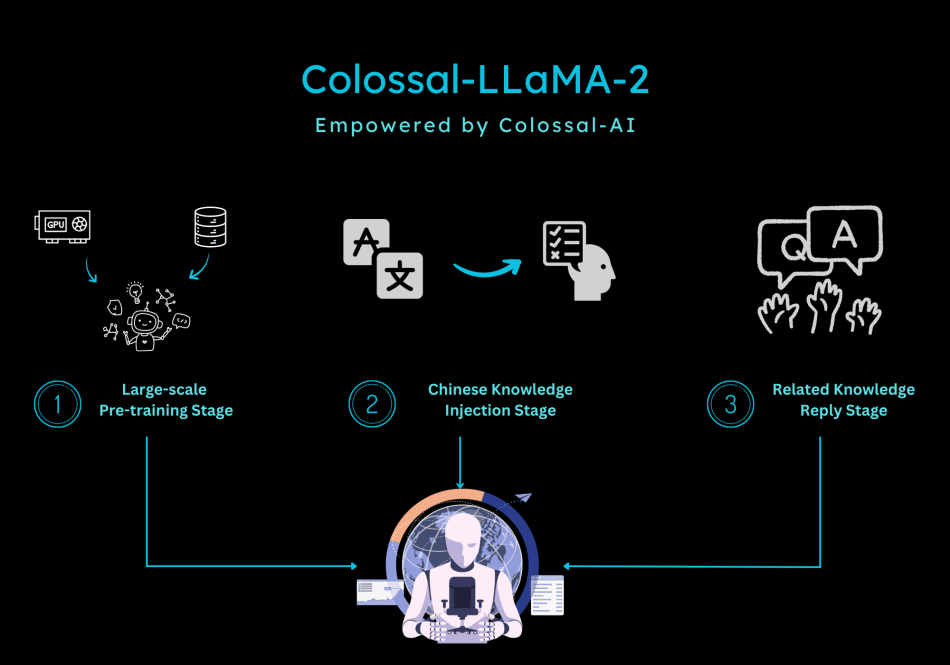
- Large-Scale Pre-training Stage: The goal at this stage is to enable the model to produce relatively smooth text through training with a large amount of corpus. This stage is completed by LLaMA-2. After this stage, the model has already mastered a large amount of English knowledge and can produce smooth results based on Next Token Prediction.
- Chinese Knowledge Injection Stage: This stage relies on high-quality Chinese knowledge. On one hand, it enhances the model’s grasp of Chinese knowledge, and on the other hand, it improves the model’s understanding of the newly added words in the Chinese vocabulary.
- Relevant Knowledge Replay Stage: This stage is dedicated to enhancing the model’s understanding and generalization ability of knowledge and alleviating the catastrophic forgetting problem.
The multi-stage approach complements each other, ultimately ensuring that the model progresses equally in both Chinese and English abilities.
Bucket Training
Continual pre-training is extremely sensitive to data distribution, so balance is particularly important. To ensure a balanced distribution of data, the Colossal-AI team designed a data bucketing strategy, dividing the same type of data into 10 different bins. During the training process, each data bucket contains one bin of each type of data, thereby ensuring that each type of data can be utilized evenly by the model.
Evaluation System
To better assess the performance of the model, the Colossal-AI
team has built a complete evaluation system – ColossalEval,
which evaluates large language models from multiple dimensions.
The framework and code of the process are fully open-source,
supporting the reproduction of results and also allowing users
to customize datasets and evaluation methods according to the
application scenario. The characteristics of the evaluation
framework are summarized as follows:
- It includes common datasets for evaluating knowledge reserve capability of large language models, such as MMLU, CMMLU, etc. For formats like multiple-choice questions and comparing probabilities of ABCD, more comprehensive calculation methods are added, such as absolute matching, single-choice perplexity, etc. This aims to measure the model’s grasp of knowledge more thoroughly.
- Support evaluation for multiple-choice questions and long-text assessments.
- Support evaluation methods for different application scenarios including multi-turn dialogues, role-playing, information extraction, content generation, etc. Users can selectively assess different aspects of the model’s abilities based on their specific needs. Additionally, the system supports the extension of custom prompts and evaluation methods to cater to individual preferences and requirements.
Bridging from General Large Models to Domain-specific Large Models
From the experience of the Colossal-AI team, constructing a Chinese version of LLaMA-2 can be summarized into the following process:
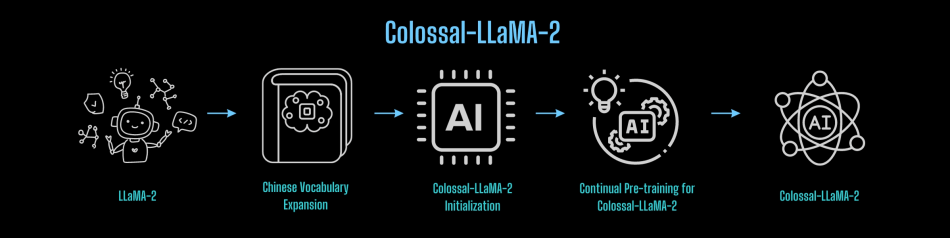
So, can this process be reused?
The answer is
affirmative, and it holds great significance in real-world
implementation scenarios.
As the wave of artificial
intelligence driven by ChatGPT surges, major internet giants, AI
companies, startups, universities, research institutions, and
others are all actively participating in the race of large
general-purpose models. However, behind the generality of these
large models often lies a lack of domain-specific knowledge.
Consequently, the issue of practical applicability becomes
particularly serious. While fine-tuning for specific
applications can yield some benefits, the absence of
domain-specific large models creates performance bottlenecks in
application deployment.
If a domain-specific large
model can be rapidly and cost-effectively constructed, followed
by fine-tuning for specific business needs, it would undoubtedly
advance the deployment of applications, providing a competitive
advantage.
Applying the above process to perform
knowledge transfer in
any field allows for the cost-effective construction of
lightweight domain-specific foundational large models:
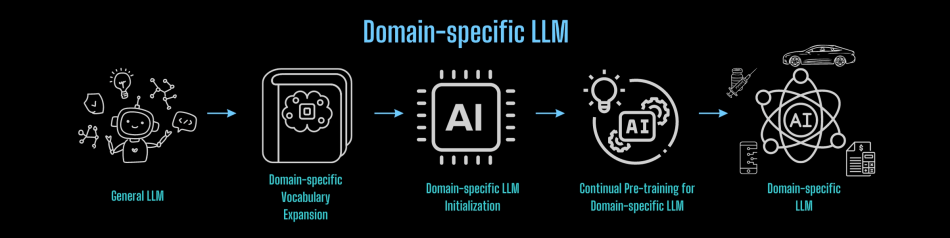
For constructing foundational large models from scratch, one can
also draw inspiration from the aforementioned experiences and
Colossal-AI’s cost-reduction and efficiency-enhancing
capabilities to efficiently achieve this goal at minimal
cost.
System Optimization
The impressive performance and cost advantages of
Colossal-LLaMA-2 are built upon the foundation of the low-cost
AI large model development system, Colossal-AI.
Colossal-AI,
based on PyTorch, leverages efficient multi-dimensional
parallelism, heterogeneous memory, and other techniques to
reduce the development and deployment costs of AI large model
training, fine-tuning, and inference. It enhances model task
performance, reduces GPU requirements, and more. In just over a
year, it has garnered over 30,000 GitHub stars within the
open-source community. It ranks first in the world in the field
of large model development tools and communities and has
collaborated with numerous Fortune 500 companies and other
well-known enterprises to develop/optimize models with hundreds
of billions or tens of billions of parameters and create
domain-specific models.
Colossal-AI Cloud Platform
To further enhance the efficiency of large model development and deployment, Colossal-AI has been upgraded to the Colossal-AI cloud platform. This platform allows users to train, fine-tune, and deploy large models at a low cost on the cloud through low-code/no-code methods while quickly integrating models for personalized applications.

Currently, the Colossal-AI cloud platform has pre-installed
mainstream models and solutions including Stable diffusion and
LLaMA-2. Users only need to upload their own data for
fine-tuning, and can deploy their fine-tuned models as APIs.
Users
can utilize GPU resources like A10, A100, H100, etc at
affordable prices, without maintaining computational clusters
and various infrastructures. More application scenarios, various
fields, different versions of models, and enterprise private
platform deployments are continuously being iterated.
The
ColossalAI cloud platform is now in public beta, and
registration will provide you with vouchers. We
welcome participation and feedback.
Colossal-AI Cloud
Platform:
platform.colossalai.com
Colossal-AI Open Source Address:
https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI

We know you don’t want to miss any news or research breakthroughs. Subscribe to our popular newsletter Synced Global AI Weekly to get weekly AI updates.
Fascinating strides in cost effective model training. The Colossal AI teams commitment to transparency and their achievement in enhancing language proficiency while keeping costs low is commendable.
Affordable Limo Rental Company for Prom Events in Jupiter FL