The continuous scaling of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 and PaLM-2, with an increasing number of parameters, has revealed unprecedented emergent abilities, most notably the remarkable capacity for zero-shot reasoning. As these models evolve and gain more power, researchers are now delving into the possibility of these models autonomously supervising their behavior or even guiding other AI models.
Previous studies have demonstrated that by sampling output from an initial model, student models can be trained to emulate the style of their teachers. However, these student models often fall short in terms of reasoning and comprehension skills compared to their larger foundation models.
In June 2023, a Microsoft research team addressed this challenge by introducing Orca, a 13-billion parameter model designed to mimic the reasoning process of large foundation models (LFMs). Orca outperformed conventional instruction-tuned models on benchmarks like BigBench Hard and AGIEval.
Continuing along this trajectory, Microsoft has recently unveiled Orca 2 in a new paper titled “Orca 2: Teaching Small Language Models How to Reason.” The focus of this release is to explore how enhanced training signals can augment the reasoning abilities of smaller language models. Notably, Orca 2 surpasses models of similar size, achieving performance levels comparable to or better than models 5-10 times larger.

Orca 2’s objectives are twofold. Firstly, researchers aim to instruct smaller models in utilizing a suite of reasoning techniques, including step-by-step processing and recall-then-generate. Secondly, they aspire to assist these models in determining the most effective reasoning strategy for a given task, enabling optimal performance regardless of their size.
Similar to its predecessor, Orca 1, the team leverages more capable LLMs to showcase various reasoning strategies across tasks. However, in Orca 2, these strategies are meticulously tailored to each task, considering the capabilities of the student model.
A notable technique employed in Orca 2 is Prompt Erasure, making it a Cautious Reasoner. This technique enables the model not only to execute specific reasoning steps but also to strategize at a higher level in approaching a task. Instead of blindly imitating powerful LLMs, the team treats them as a repository of behaviors from which they judiciously select those best suited for the task at hand.
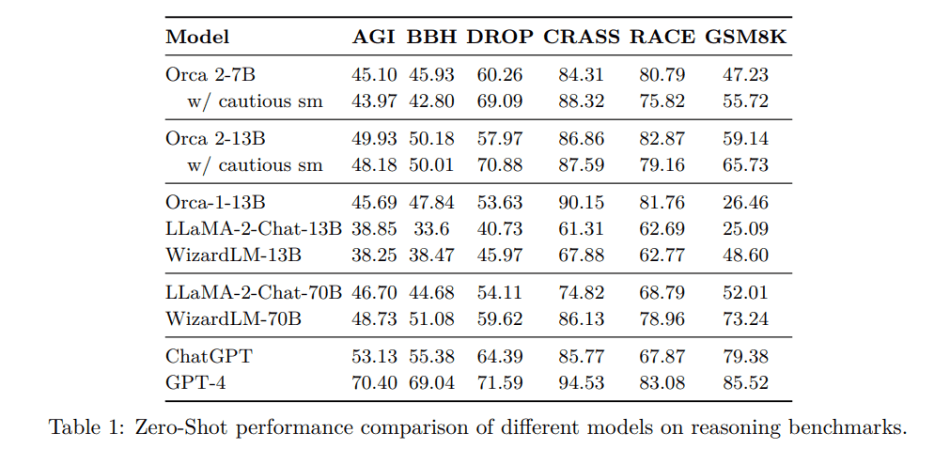
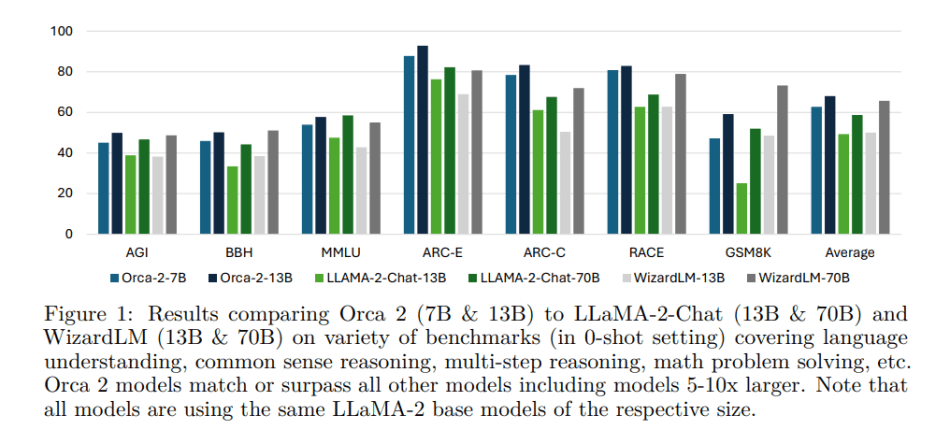
In their empirical study, the researchers comprehensively evaluate Orca 2 on 15 benchmarks, covering approximately 100 tasks and over 36,000 unique prompts. The results show that Orca 2 significantly outperforms models of similar size, even matching or surpassing those 5 to 10 times larger, particularly on tasks requiring advanced reasoning.
In conclusion, this work marks a significant step forward, emphasizing the importance of teaching smaller models to reason. The research team believes that advancing the capabilities of smaller models will pave the way for new applications with different deployment scenarios and trade-offs between efficiency and capability.
The paper Orca 2: Teaching Small Language Models How to Reason on arXiv.
Author: Hecate He | Editor: Chain Zhang

We know you don’t want to miss any news or research breakthroughs. Subscribe to our popular newsletter Synced Global AI Weekly to get weekly AI updates.
0 comments on “Microsoft Orca 2’s Triumph: Comparable or Superior Performance to Models 5-10x Its Size in Mastering Reasoning Tasks”