Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across various tasks. However, they often grapple with a limited context window size due to the high costs of fine-tuning, scarcity of lengthy texts, and the introduction of catastrophic values by new token positions.
To address this issue, in a new paper LongRoPE: Extending LLM Context Window Beyond 2 Million Tokens, a Microsoft research team introduces LongRoPE, a pioneering method that extends the context window of pre-trained LLMs to an impressive 2048k tokens while preserving performance at the original short context window.

The team identifies four major obstacles hindering further extension of the context window:
- Untrained new position indices introduce numerous catastrophic values, leading to out-of-distribution issues and complicating fine-tuning convergence.
- Fine-tuning typically necessitates texts of corresponding lengths, yet lengthy texts, especially those surpassing 1000k, are scarce.
- Training on extra-long texts is computationally demanding, requiring extensive training hours and GPU resources.
- Extending to extremely long context windows disperses attention thinly across numerous token positions, thereby degrading performance on the original short context.
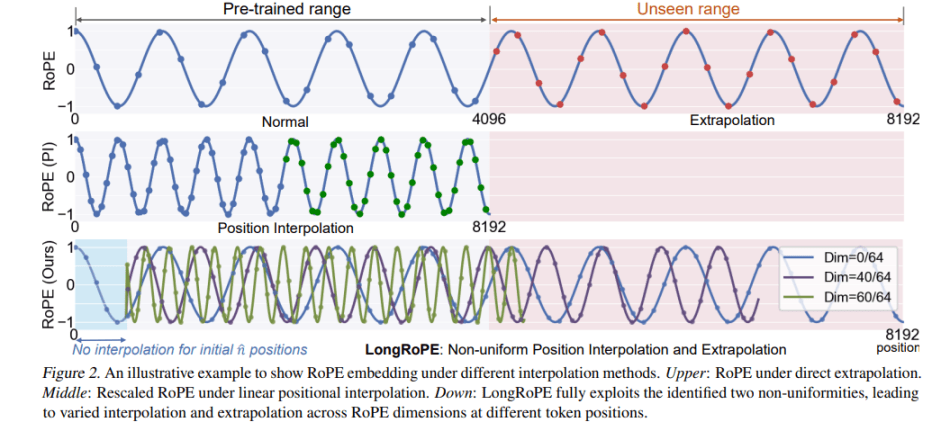
To overcome the first challenge, the team employs interpolated RoPE positional embedding, which scales down new position indices to the pre-trained range. They empirically unveil two key findings:
- Effective positional interpolation should account for two forms of nonuniformities: varying RoPE dimensions and token positions.
- By integrating non-uniformities into positional interpolation, they effectively retain information in the original RoPE, particularly crucial dimensions and token positions.
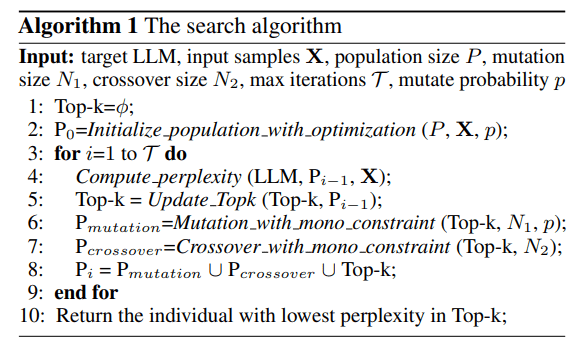
Motivated by these findings, LongRoPE is developed, successfully extending the LLM context window beyond 2 million tokens through three key innovations:
- Identification and exploitation of two forms of non-uniformities in positional interpolation via efficient search, providing enhanced initialization for fine-tuning and enabling an 8× extension in non-fine-tuning scenarios.
- Introduction of a progressive extension strategy, initially fine-tuning a 256k length LLM, followed by a second positional interpolation on the fine-tuned extended LLM to achieve a 2048k context window.
- Readjustment of LongRoPE on 8k length to restore performance in the short context window.
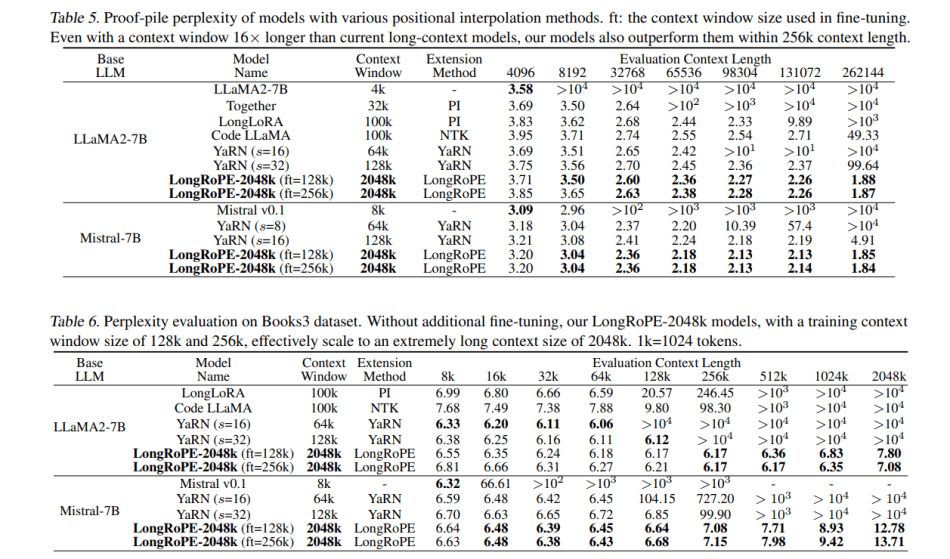
Extensive experiments across different LLMs and various long-context tasks underscore the effectiveness of LongRoPE. It maintains low perplexity from 4k to 2048k evaluation length, achieves over 90% passkey retrieval accuracy, and delivers comparable accuracy on standard benchmarks designed within the 4096 context window. LongRoPE can be applied to any LLMs based on RoPE embedding.
The researchers envision that LongRoPE models will enable a
plethora of new long-context applications and inspire further
research in the field.
Code will be available at
https: //github.com/microsoft/LongRoPE. The paper
LongRoPE: Extending LLM Context Window Beyond 2 Million
Tokens is on arXiv.
Author: Hecate He | Editor: Chain Zhang

We know you don’t want to miss any news or research breakthroughs. Subscribe to our popular newsletter Synced Global AI Weekly to get weekly AI updates.

Pingback: Microsoft’s LongRoPE Breaks the Limit of Context Window of LLMs, Extents it to 2 Million Tokens | Windows – Buy Aussie News | Aussie general news blog
Pingback: Dawn of the Infinite Context Window - The Media Copilot
The challenges mentioned, such as the high costs of fine-tuning and scarcity of lengthy texts, are well-acknowledged in the field. LongRoPE not only recognizes these tunnel rush challenges but offers a viable solution, demonstrating a thoughtful approach to overcoming obstacles in large language models.